Spherical Mirrors
Spherical Mirrors: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Spherical Mirrors, Concave Mirror, Image Distance & Curved Mirrors etc.
Important Questions on Spherical Mirrors
Focal length of diverging mirror is . An object is kept at a distance of from the mirror. Find the image distance and it's nature.
When a spherical mirror is held up almost facing the sun, a sharp image of the sun is formed on a small piece of paper, which causes it to catch fire. The spherical mirror is _____ in nature and the sheet of paper is placed at the _____ of the mirror. Fill in the blanks by choosing an appropriate option from the ones given below.
The light that reaches the telescopes comes from very far away celestial objects. Draw a ray diagram to show what happens when light from a far away object falls on a convex mirror and a concave mirror.
A student determines the focal length of a device 'X' by focusing the image of a distant object on a screen placed from the device on the same side as the object. The device 'X' is
Write a short note on the image formation by convex mirror.
Shilpi places a spherical mirror of radius in glycerine. Its focal length in air and glycerine differ by _____.
If the length of the object is then find the length of the image. Given that the focal length of the mirror is .
Name the mirror which can show the size of the object to be double of its original.
Image of an object situated at a distance of from a convex mirror is formed at a distance of from the mirror. Find the focal length of convex mirror.
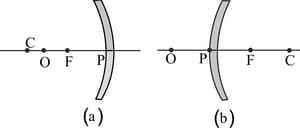
In the given figures, locate the image formed by using an appropriate ray diagram of a point object O shown in the figure using laws of reflection.
What will be magnification when object is at infinity in front of a concave mirror.
A high object is placed at a distance of from a convex mirror of focal length . Find the position, size and nature of the image formed by the mirror.
The distance between a real object and its image in a convex mirror of focal length is . Find the size of the image, if the object size is .
A dentist uses a spherical mirror that produces an upright image that is magnified four times. What kind of mirror is it? What is its focal length in terms of the object distance?
(i) Find the focal length of a convex mirror whose radius of curvature is .
(ii) A concave mirror produces three times magnified (enlarged) real image of an object placed at in front of it. Where is the image located?
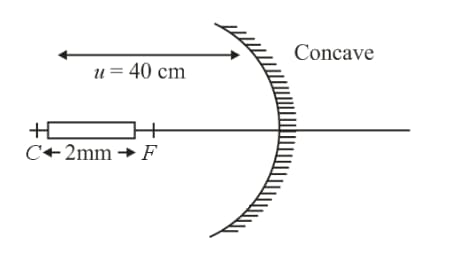
A concave mirror has a focal length of . A rod of length is placed along the principal axis of the mirror in such a way that the end closer to the mirror lies on its centre of curvature. The length of the image of the rod is
Your friend noted the measurements of object distance and image distance in an experiment with a concave mirror and made a conclusion. What would be his conclusion?
List out the material required and write the experimental procedure to find the image distance using concave mirror when an object is kept in front of it on its principal axis at different locations.
Why do we use only mercury and lead oxide to make a spherical mirror?
We might have observed that convex mirrors are used in vehicles as rearview mirrors. Convex mirrors are preferred as rearview mirrors because they always produce erect image and has a large field of view compared to plane mirrors. We might have also observed the note written on rearview mirrors saying that objects appearing in the mirror are closer than they appear. Let’s understand how far/close they look in a rearview mirror with this case study.
If we replace the convex mirror with a concave mirror of radius of curvature and the vehicle is still at a distance of from the mirror,
